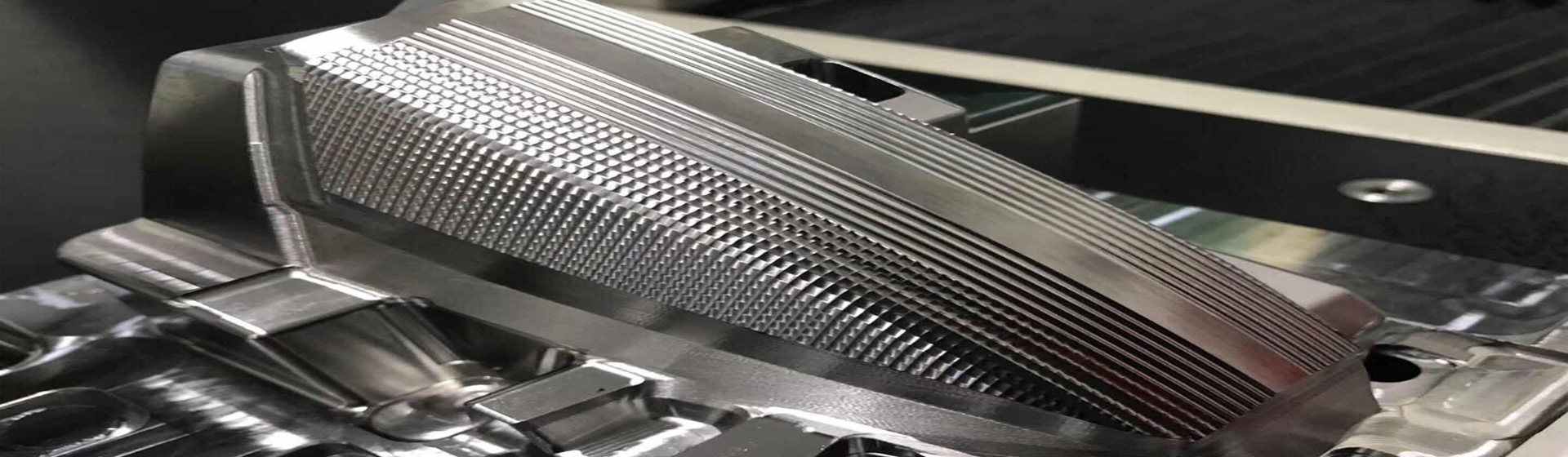
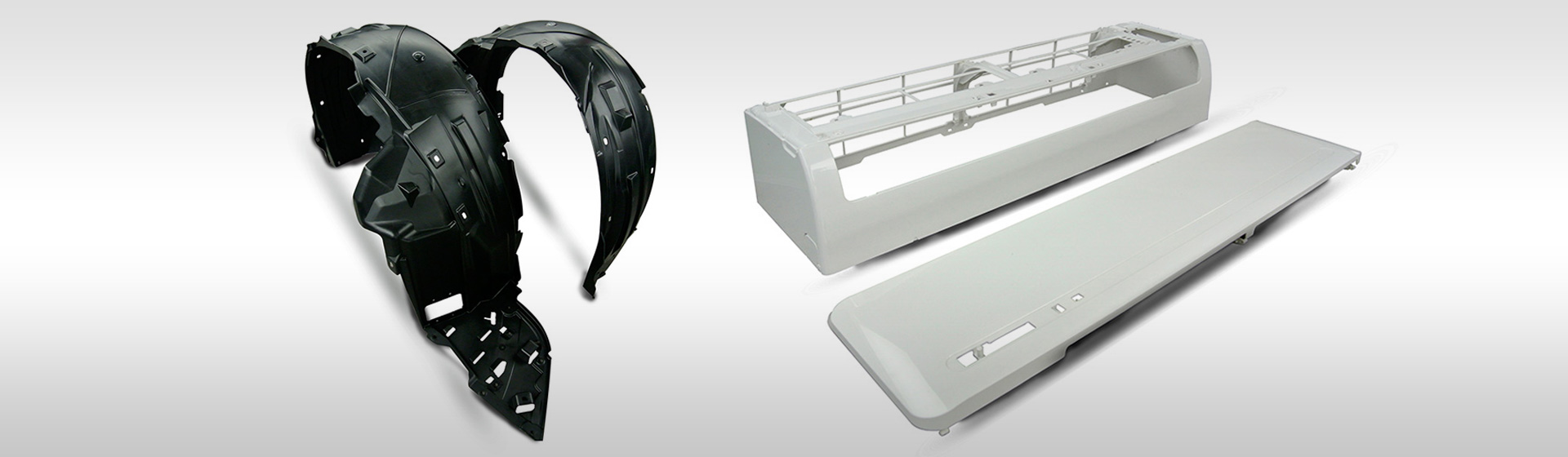
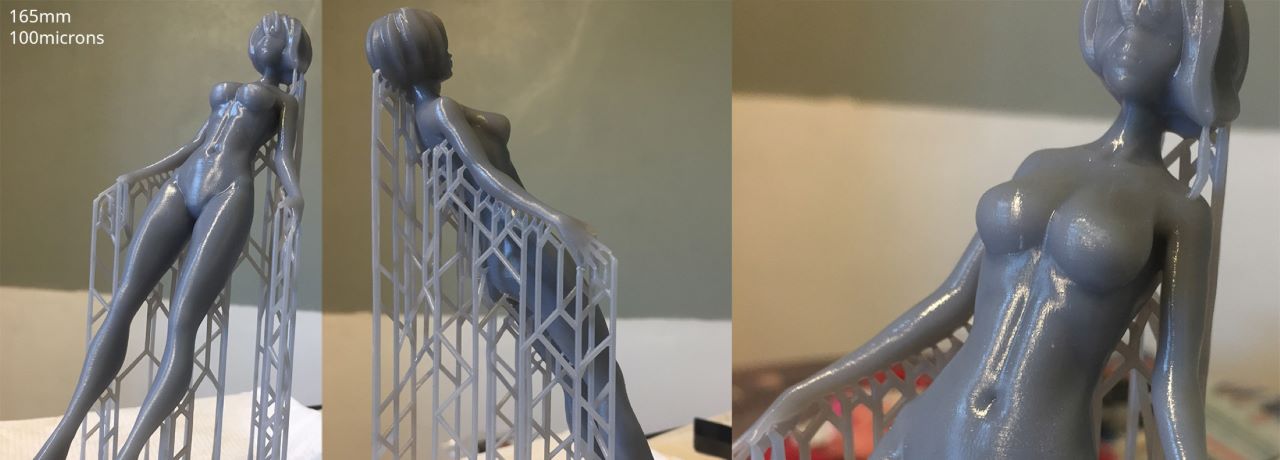
Looking for more than a desktop 3D printer can provide? Need an alternative to your in-house capabilities? Our industrial 3D printing service ensures accuracy and repeatability so you get highly precise partsí¬every time. At GTS, additive manufacturing is designed for functional prototypes, complex designs, and production components in as fast as 1 day.
Which 3D Printing Process Should I Use?
Stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA) is an industrial 3D printing process used to create concept models, cosmetic prototypes, and complex parts with intricate geometries in as fast as 1 day. A wide selection of materials, extremely high feature resolutions, and quality surface finishes are possible with SLA.
How Does Stereolithography Work?
The SLA machine begins drawing the layers of the support structures, followed by the part itself, with an ultraviolet laser aimed onto the surface of a liquid thermoset resin. After a layer is imaged on the resin surface, the build platform shifts down and a recoating bar moves across the platform to apply the next layer of resin. The process is repeated layer by layer until the build is complete.
Newly built parts are taken out of machine and into a lab where solvents are used to remove any additional resins. When the parts are completely clean, the support structures are manually removed. From there, parts undergo a UV-curing cycle to fully solidify the outer surface of the part. The final step in the SLA process is the application of any custom or customer-specified finishing. Parts built in SLA should be used with minimal UV and humidity exposure so they doní»t degrade.
Selective Laser Sintering
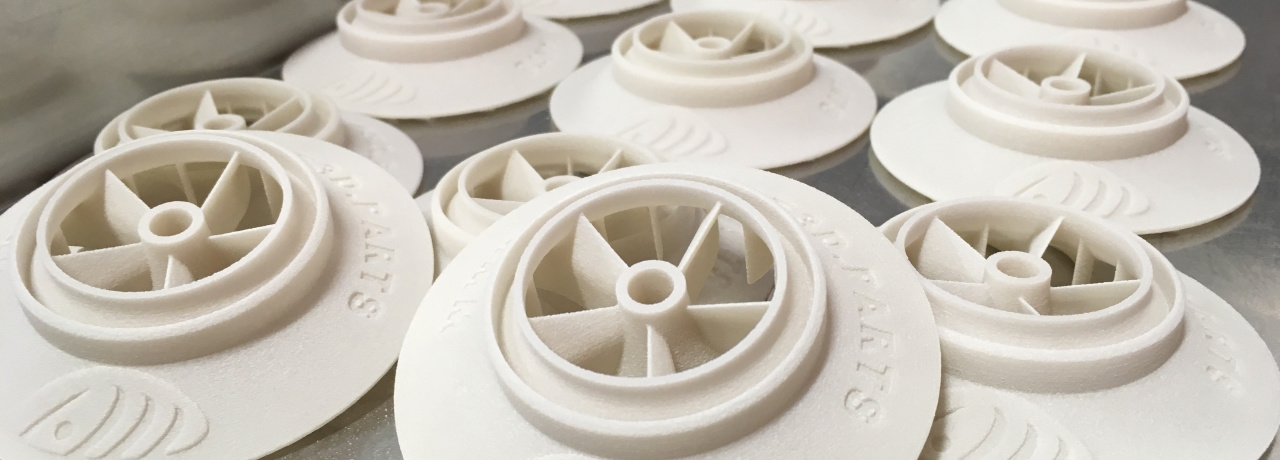

Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an industrial 3D printing process that produces accurate prototypes and functional production parts in as fast as 1 day. Multiple nylon-based materials are available, which create highly durable final parts.
How Does Selective Laser Sintering Work?
The SLS machine begins sintering each layer of part geometry into a heated bed of nylon-based powder. After each layer is fused, a roller moves across the bed to distribute the next layer of powder. The process is repeated layer by layer until the build is complete. When the build finishes, the entire powder bed with the encapsulated parts is moved into a breakout station, where it is raised up, and parts are broken out of the bed. An initial brushing is manually administered to remove a majority of loose powder. Parts are then bead blasted to remove any of the remaining residual powder before ultimately reaching the finishing department.